MSSQL auditing is configured separately from Windows auditing. To audit MSSQL you need to create an audit and then assign a server audit specification. See screenshots for visuals:
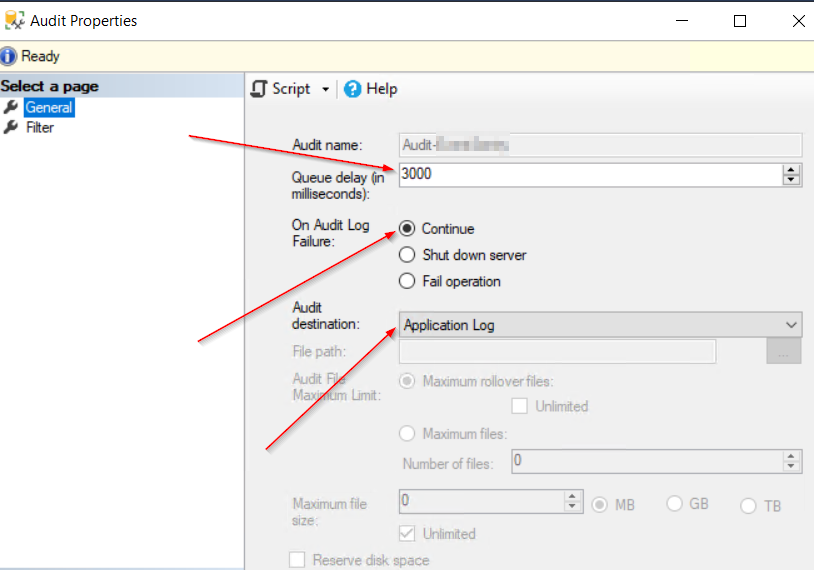
Create an audit, change the queue delay to something like 3000, set audit log to continue on failure, and send the events to the application log. If you want to be more secure you can set it to be sent to the security event log.
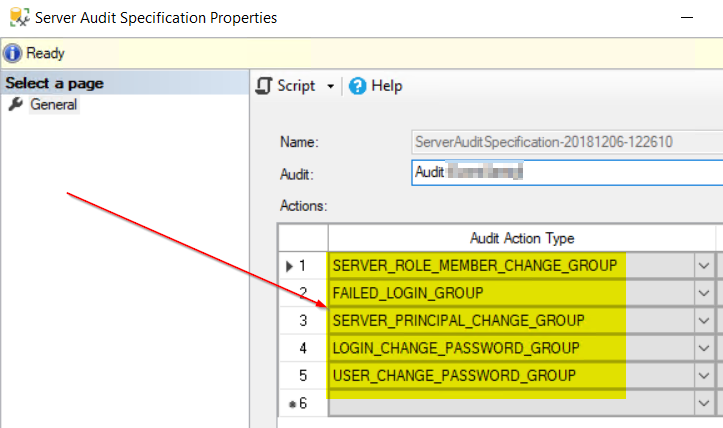
Next create the audit specifications. I added these audit action types to my specifications.
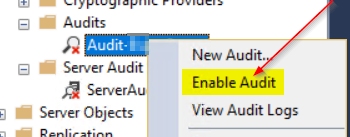
Next you need to enable the audit and audit specs by right clicking them.
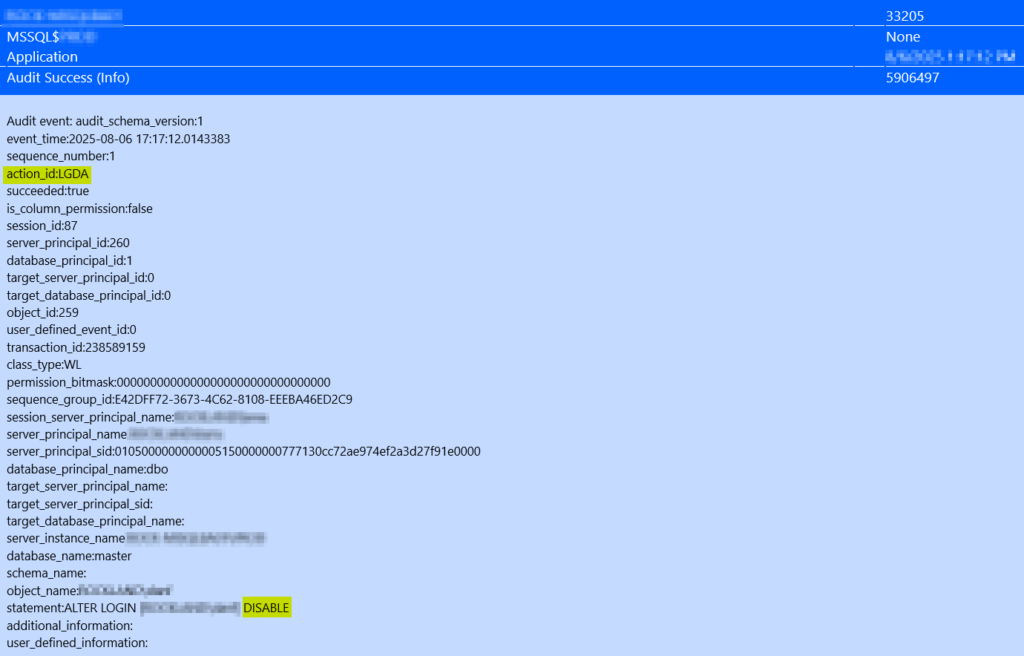
The Windows event ID you will want to look for is Event Source:
Log: Application
Severity: Audit Sucess
Event Source: MSSQL*
Event ID: 33205
Content Filter Regex:
action_id\:PWU
action_id\:LGDA
action_id\:LGEA
action_id\:DL
action_id\:DR
action_id\:CR
action_id\:APRL
action_id\:DPRL
action_id\:LGIS
Here is a screen shot of an email alert I have set for disabling a user in MSSQL.